Visual Studio Code¶
Visual Studio Code is a free cross-platform code editor by Microsoft (not to be confused with Visual Studio).
Importing the project¶
Make sure the C/C++ extension is installed. You can find instructions in the official documentation. Alternatively, clangd can be used instead.
When using the clangd extension, run
scons compiledb=yes.From the Visual Studio Code's main screen open the Godot root folder with File > Open Folder....
Press Ctrl + Shift + P to open the command prompt window and enter Configure Task.
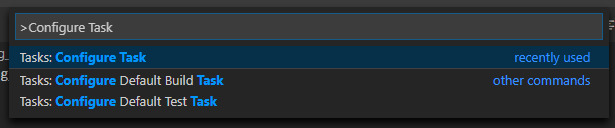
Select the Create tasks.json file from template option.
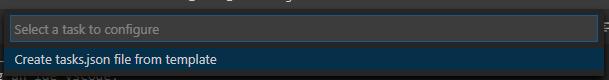
Then select Others.
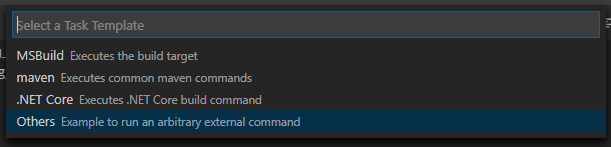
If there is no such option as Create tasks.json file from template available, either delete the file if it already exists in your folder or create a
.vscode/tasks.jsonfile manually. See Tasks in Visual Studio Code for more details on tasks.Within the
tasks.jsonfile find the"tasks"array and add a new section to it:{ "label": "build", "group": "build", "type": "shell", "command": "scons", "args": [ // enable for debugging with breakpoints "dev_build=yes", ], "problemMatcher": "$msCompile" }
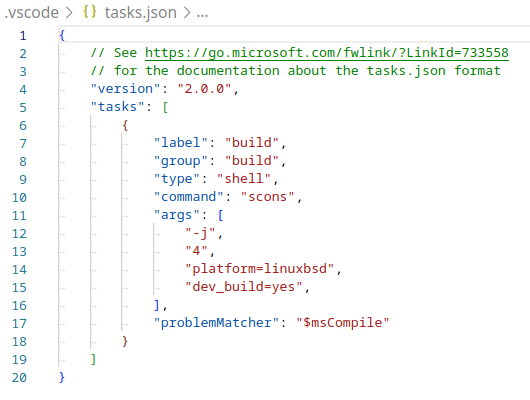
An example of a filled out tasks.json.¶
Arguments can be different based on your own setup and needs. See Introduction to the buildsystem for a full list of arguments.
Debugging the project¶
To run and debug the project you need to create a new configuration in the launch.json file.
Press Ctrl + Shift + D to open the Run panel.
If
launch.jsonfile is missing you will be prompted to create a new one.
Select C++ (GDB/LLDB). There may be another platform specific option here. If selected, adjust the configuration example provided accordingly.
Within the
launch.jsonfile find the"configurations"array and add a new section to it:
{
"name": "Launch Project",
"type": "lldb",
"request": "launch",
// Change to godot.linuxbsd.tools.64.llvm for llvm-based builds.
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/godot.linuxbsd.editor.dev.x86_64",
// Change the arguments below for the project you want to test with.
// To run the project instead of editing it, remove the "--editor" argument.
"args": [ "--editor", "--path", "path-to-your-godot-project-folder" ],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"preLaunchTask": "build"
}
{
"name": "Launch Project",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
// Change to godot.linuxbsd.tools.64.llvm for llvm-based builds.
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/godot.linuxbsd.editor.dev.x86_64",
// Change the arguments below for the project you want to test with.
// To run the project instead of editing it, remove the "--editor" argument.
"args": [ "--editor", "--path", "path-to-your-godot-project-folder" ],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"setupCommands":
[
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "build"
}
{
"name": "Launch Project",
"type": "cppvsdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/bin/godot.windows.editor.dev.x86_64.exe",
// Change the arguments below for the project you want to test with.
// To run the project instead of editing it, remove the "--editor" argument.
"args": [ "--editor", "--path", "path-to-your-godot-project-folder" ],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"console": "internalConsole",
"visualizerFile": "${workspaceFolder}/platform/windows/godot.natvis",
"preLaunchTask": "build"
}
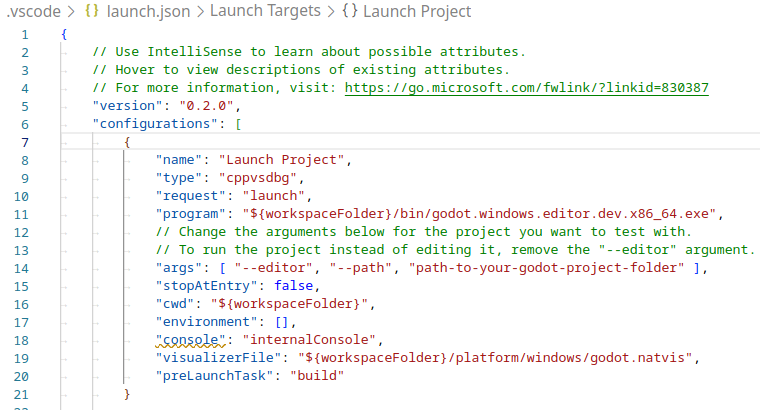
An example of a filled out launch.json.¶
Note
Due to sporadic performance issues, it is recommended to use LLDB over GDB on Unix-based systems. Make sure that the CodeLLDB extension is installed.
If you encounter issues with lldb, you may consider using gdb (see the LinuxBSD_gdb configuration).
Do note that lldb may work better with LLVM-based builds. See Compiling for Linux, *BSD for further information.
The name under program depends on your build configuration,
e.g. godot.linuxbsd.editor.dev.x86_64 for 64-bit LinuxBSD platform with
platform=editor and dev_build=yes.
If you run into any issues, ask for help in one of Godot's community channels.
Tip
To get linting on class reference XML files, install the vscode-xml extension.